diff --git a/conf.py b/conf.py
index 1fd961a6..8554f1d9 100644
--- a/conf.py
+++ b/conf.py
@@ -78,6 +78,8 @@
#
html_theme = 'furo'
html_logo = 'assets/logo/OpenMS_transparent_background.png'
+html_favicon = 'assets/logo/OpenMS_transparent_background.png'
+
html_theme_options = {
"navigation_with_keys": True,
"light_css_variables": {
@@ -90,7 +92,6 @@
pygments_dark_style = 'rrt'
-
# Add any paths that contain custom static files (such as style sheets) here,
# relative to this directory. They are copied after the builtin static files,
# so a file named "default.css" will overwrite the builtin "default.css".
diff --git a/docs/contribute-to-openms/adding-new-tool-to-topp.md b/docs/contribute-to-openms/adding-new-tool-to-topp.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..36b9082c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/contribute-to-openms/adding-new-tool-to-topp.md
@@ -0,0 +1,100 @@
+Adding New Tool to The TOPP suite
+=====================================
+
+## The OpenMS pipeline (TOPP)
+
+Any tool that is written with the OpenMS library can easily be made into a TOPP tool by simply using the OpenMS command
+line parser which is able to parse ParamXML, a powerful XML based description of the tool. Hence most analysis algorithms
+in OpenMS are available as a stand-alone tool which can be called on the command line or integrated into workflow engines
+via the CTD mechanism. A current list of TOPP tools can be found in [the documentation](https://abibuilder.informatik.uni-tuebingen.de/archive/openms/Documentation/release/latest/html/TOPP_documentation.html).
+
+## What do I have to do to add a new TOPP tool?
+
+The recommended way is to inherit from the class TOPPBase as in existing TOPP tools (sources available in /src/topp/). This will add command line parsing functionality to your tool as described in the TOPP section of this page.
+
+- Add the code to `src/topp/` and register it in `src/topp/executables.cmake`
+- Add your tool (with the correct category) to `getTOPPToolList()` in `src/openms/source/APPLICATIONS/ToolHandler.cpp`.
+ This creates a doxygen page with the `–help` output of the tool (using `TOPPDocumenter`). This page must be included
+ at the end of the doxygen documentation of your tool (see other tools for an example).
+- Add it to the TOPP docu page (in `doc/doxygen/public/TOPP.doxygen`)
+- Add the name to `src/topp/executables.cmake`
+- Write a TOPP test (add it to `src/tests/topp/CMakeLists.txt`)
+
+```{warning}
+Handle any kind of input files to your TOPP tool via command line flags and use the `${DATA_DIR_TOPP}` prefix. Use
+ini-files to specify output-files, but not input-files. Doing otherwise will break out-of-source builds.
+```
+
+```{hint}
+add `-test` to the call of your TOPP tool and also create the expected output that you put in `src/tests/topp` with that
+flag active. The flag ensures that UniqueId's, dates etc are equal no matter where and when the tool is run.
+```
+
+## What do I have to do to add a new UTILS tool?
+
+- Add the code to `src/utils/` and register it in `src/utils/executables.cmake`.
+- Add your tool to `getUtilList()` in `src/openms/source/APPLICATIONS/ToolHandler.cpp`. This creates a doxygen page with
+ the `–help` output of the tool (using `TOPPDocumenter`). This page must be included at the end of the doxygen
+ documentation of your tool (see other tools for an example).
+- Add it to the UTILS docu page (in `doc/doxygen/public/UTILS.doxygen`)
+- Write a test (this is optional for UTILS). See TOPP tools above and add the test to the bottom of `src/tests/topp/CMakeLists.txt`.
+
+## I want to implement a new file adapter. What is to be done?
+
+First, add a file adapter class to the `include/OpenMS/FORMAT/` and `source/FORMAT/` folders. The file adapter should
+implement a default constructor, a load method and a store method. Make sure your code conforms to the OpenMS Coding
+conventions. For automatic file type recognition, you need to
+
+- register your new file type at the Type enum in `/include/OpenMS/FORMAT/FileTypes.h`,
+- flag the file type as supported in the isSupported method of `/source/FORMAT/FileHandler.C`
+- register the file extension in the getTypeByFileName method of `/source/FORMAT/FileHandler.C`
+
+If the new file is a peak or feature file format you should also add it to loadExperiment or loadFeatures, respectively,
+of the FileHandler class. To add the file format to the TOPPView open dialog, you have to modify the file
+`/source/APPLICATIONS/TOPPViewBase.C`.
+
+- Add the file extensions to the filter_all and filter_single variables of the getFileList_ method.
+
+To add your format to TOPP applications:
+
+- add the file extension to the extensions list of the respective parameter:
+ ```
+ e.g. setValidStrings_("in_type", StringList::create("mzData,mzXML,mzML")); in FileInfo
+ ```
+
+## How to create an icon file for a TOPP tool under Windows?
+
+- Create an .ico file: first, you need some graphics program (The GIMP is recommended) think of a motive and remind
+ yourself that you have limited space. Create at least a 16x16, 32x32, 48x48 and 64x64 pixel version and save each of
+ them in a separate layer of the respective size. Do not add any larger sized layers, since Win XP will not display any
+ icon then. When saving the image as type `.ico` the GIMP will ask you for the color depth of each layer. As it is
+ recommended to have multiple color depths of each icon-size, go back to the layers and duplicate each layer twice.
+ That should give you 12 layers. Now, save the image as `.ico` (e.g. TOPPView.ico) file, giving each group of equal
+ sized layers a 32 bit (8 bit transparency), 8 bit (1 bit transparency), 4 bit (1 bit transparency) color depth.
+
+```{attention}
+Make sure to assign the higher color depth to the upper layers as Windows will not pick the highest possible color
+otherwise.
+```
+
+- Create a resource file: Create a text file named `.rc` (e.g. TOPPView.rc) Insert the following line: 101 ICON
+ "TOPPView.ico" , replacing TOPPView with your binary name. Put both files in `OpenMS/source/APPLICATIONS/TOPP/`
+ (similar files for other TOPP tools already present). Re-run cmake and re-link your TOPP tool.
+
+Voila. You should have an iconized TOPP tool.
+
+## Develop your Tool in an external project using OpenMS
+
+To include the OpenMS library in one of your projects, we recommend to have a look at a small emulated external project
+in our repository. We strongly suggest to use CMake for building your project together with OpenMS to make use of the
+macros and environment information generated during the build of the OpenMS library.
+
+## The Common Tool Description (CTD)
+
+The CTD is a format developed from the OpenMS team to allow the user to use TOPP tools also in other workflow engines.
+Each tool can output a CTD description of itself (the XML scheme for the CTD can be found here), which can then be used
+by a node generator program to generate nodes for different workflow engines. The CTD mechanism is shared by OpenMS with
+other mature libraries like SeqAn and BALL. An example for a node generation program are the Generic KNIME Nodes. The
+most complete description on how to generate your own Generic KNIME Nodes based on a CTD (e.g. from your freshly
+developed command line tool), can be found on the SeqAn documentation. We are working on a tutorial specifically
+tailored to OpenMS.
diff --git a/docs/contribute-to-openms/advanced.md b/docs/contribute-to-openms/advanced.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..58552ada
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/contribute-to-openms/advanced.md
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
+Advanced
+========
+```{toctree}
+:maxdepth: 1
+
+advanced/developer-guidelines-for-adding-new-dependent-libraries.md
+advanced/build-custom-knime-plugin.md
+advanced/custom-compilation.md
+
+```
diff --git a/docs/contribute-to-openms/advanced/build-custom-knime-plugin.md b/docs/contribute-to-openms/advanced/build-custom-knime-plugin.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e69de29b
diff --git a/docs/advanced-resources/custom-compilation.md b/docs/contribute-to-openms/advanced/custom-compilation.md
similarity index 100%
rename from docs/advanced-resources/custom-compilation.md
rename to docs/contribute-to-openms/advanced/custom-compilation.md
diff --git a/docs/additional-resources/developer-guidelines-for-addding-new-dependent-libraries.md b/docs/contribute-to-openms/advanced/developer-guidelines-for-adding-new-dependent-libraries.md
similarity index 100%
rename from docs/additional-resources/developer-guidelines-for-addding-new-dependent-libraries.md
rename to docs/contribute-to-openms/advanced/developer-guidelines-for-adding-new-dependent-libraries.md
diff --git a/docs/additional-resources/openms-git-workflow.md b/docs/contribute-to-openms/openms-git-workflow.md
similarity index 100%
rename from docs/additional-resources/openms-git-workflow.md
rename to docs/contribute-to-openms/openms-git-workflow.md
diff --git a/docs/additional-resources/pull-request-checklist.md b/docs/contribute-to-openms/pull-request-checklist.md
similarity index 100%
rename from docs/additional-resources/pull-request-checklist.md
rename to docs/contribute-to-openms/pull-request-checklist.md
diff --git a/docs/additional-resources/reporting-bugs-and-issues.md b/docs/contribute-to-openms/reporting-bugs-and-issues.md
similarity index 100%
rename from docs/additional-resources/reporting-bugs-and-issues.md
rename to docs/contribute-to-openms/reporting-bugs-and-issues.md
diff --git a/docs/additional-resources/write-and-label-github-issues.md b/docs/contribute-to-openms/write-and-label-github-issues.md
similarity index 100%
rename from docs/additional-resources/write-and-label-github-issues.md
rename to docs/contribute-to-openms/write-and-label-github-issues.md
diff --git a/docs/develop-with-openms/api-reference.md b/docs/develop-with-openms/api-reference.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..bcb43b41
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/develop-with-openms/api-reference.md
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
+API Reference
+=============
diff --git a/docs/develop-with-openms/build-openms-from-source.md b/docs/develop-with-openms/build-openms-from-source.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..83b89946
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/develop-with-openms/build-openms-from-source.md
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
+Build OpenMS from Source
+========================
diff --git a/docs/develop-with-openms/developer-tutorial.md b/docs/develop-with-openms/developer-tutorial.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..df47ade2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/develop-with-openms/developer-tutorial.md
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
+Developer Tutorial
+==================
diff --git a/docs/additional-resources/external-code-using-openms.md b/docs/develop-with-openms/link-external-code-to-openms.md
similarity index 100%
rename from docs/additional-resources/external-code-using-openms.md
rename to docs/develop-with-openms/link-external-code-to-openms.md
diff --git a/docs/develop-with-openms/openms-core-library.md b/docs/develop-with-openms/openms-core-library.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..6e732f88
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/develop-with-openms/openms-core-library.md
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
+OpenMS C++ Core Library
+=======================
diff --git a/docs/develop-with-openms/pyopenms.md b/docs/develop-with-openms/pyopenms.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..773d3774
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/develop-with-openms/pyopenms.md
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
+pyOpenMS
+========
diff --git a/docs/graphical-topp-tools/ini-file-editor.md b/docs/graphical-topp-tools/ini-file-editor.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..541316c1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/graphical-topp-tools/ini-file-editor.md
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
+INIFileEditor
+============
+
+Can be used to visually edit INI files of TOPP tools.
+
+The values can be edited by double-clicking or pressing F2.
+
+The documentation of each value is shown in the text area on the bottom of the widget.
+
+
diff --git a/docs/graphical-topp-tools/swathwizard.md b/docs/graphical-topp-tools/swathwizard.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..22412fdd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/graphical-topp-tools/swathwizard.md
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+SwathWizard
+==========
+
+An assistant for Swath analysis.
+
+The Wizard takes the user through the whole analysis pipeline for SWATH proteomics data analysis, i.e. the
+[TOPP Documentation: OpenSwathWorkflow](https://abibuilder.informatik.uni-tuebingen.de/archive/openms/Documentation/nightly/html/UTILS_OpenSwathWorkflow.html) tool, including downstream tools such as [GitHub:PyProphet/pyProphet](https://github.com/PyProphet/pyprophet) and the [GitHub:msproteomicstools/TRIC alignment](https://github.com/msproteomicstools/msproteomicstools) tool.
+
+Since the downstream tools require Python and the respective modules, the Wizard will check their proper installation
+status and warn the user if a component is missing.
+
+Users can enter the required input data (mzML MS/MS data, configuration files) in dedicated fields, usually by drag and
+droping files from the operating systems' file explorer (Explorer, Nautilus, Finder...). The output of the Wizard is
+both the intermediate files from OpenSWATH (e.g. the XIC data in `.sqMass` format) and the tab-separated table format
+(`.tsv`) from pyProphet and TRIC.
+
+This is how the wizard looks like:
+
+
+
+A schematic of the internal data flow (all tools are called by SwathWizard in the background) can be found in the
+[TOPP Documentation: SwathWizard](https://abibuilder.informatik.uni-tuebingen.de/archive/openms/Documentation/nightly/html/TOPP_SwathWizard.html).
+
+A recommended test data for the Wizard is the [PASS00779](https://db.systemsbiology.net/sbeams/cgi/PeptideAtlas/PASS_View?identifier=PASS00779) dataset.
diff --git a/docs/graphical-topp-tools/topp.md b/docs/graphical-topp-tools/topp.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7309d620
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/graphical-topp-tools/topp.md
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
+TOPP
+===
+
+**TOPP - The OpenMS Proteomics Pipeline** is a pipeline for the analysis of HPLC-MS data. It consists of several small
+applications that can be chained to create analysis pipelines tailored for a specific problem.
+
+The TOPP tools are divided into several subgroups, like graphical tools, file handling, signal processing and
+preprocessing, quantitation, map alignment, protein/peptide identification, protein/peptide processing, targeted
+experiments and OpenSWATH, peptide property prediction, cross-linking, quality-control, among a few.
+
+Few of the graphical tools are explained below:
+
+```{toctree}
+:maxdepth: 1
+
+toppview
+toppas
+ini-file-editor
+swathwizard
+```
+
+For advanced documentation on every TOPP tool, see the [OpenMS TOPP API Reference](https://abibuilder.informatik.uni-tuebingen.de/archive/openms/Documentation/nightly/html/TOPP_documentation.html).
diff --git a/docs/graphical-topp-tools/toppas.md b/docs/graphical-topp-tools/toppas.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..cd496144
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/graphical-topp-tools/toppas.md
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
+TOPPAS
+======
+
+An assistant for GUI-driven TOPP workflow design.
+
+**TOPPAS** allows to create, edit, open, save, and run TOPP workflows. Pipelines can be created conveniently in a GUI by
+means of mouse interactions. The parameters of all involved tools can be edited within the application and are also
+saved as part of the pipeline definition in the `.toppas` file. Furthermore, TOPPAS interactively performs validity
+checks during the pipeline editing process, in order to make it more difficult to create an invalid workflow. Once set
+up and saved, a workflow can also be run without the GUI using the `ExecutePipeline` TOPP tool.
+
+The following figure shows a simple example pipeline that has just been created and executed successfully:
+
+
+
+More information about TOPPAS can be found in the [TOPPAS tutorial](../tutorials/TOPP/TOPPAS-tutorial.md).
+
+**The command line parameters of this tool are**:
+
+```bash
+TOPPAS -- An assistant for GUI-driven TOPP workflow design.
+
+Usage:
+ TOPPAS [options] [files]
+
+Options are:
+ --help Shows this help
+ --debug Enables debug messages
+ -ini Sets the INI file (default: ~/.TOPPAS.ini)
+```
diff --git a/docs/graphical-topp-tools/toppview.md b/docs/graphical-topp-tools/toppview.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0b001e51
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/graphical-topp-tools/toppview.md
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
+TOPPView
+=======
+
+**TOPPView** is a viewer for MS and HPLC-MS data. It can be used to inspect files in mzML, mzData, mzXML and several other
+file formats. It also supports viewing data from an OpenMS database. The following figure shows two instances of TOPPView
+displaying a HPLC-MS map and a MS raw spectrum:
+
+
+
+More information about TOPPView can be found in the [TOPP tutorial](../tutorials/TOPP/TOPP-tutorial.md).
+
+**The command line parameters of this tool are**:
+
+```bash
+TOPPView -- A viewer for mass spectrometry data.
+
+Usage:
+ TOPPView [options] [files]
+
+Options are:
+ --help Shows this help
+ -ini Sets the INI file (default: ~/.TOPPView.ini)
+ --force Forces scan for new tools/utils
+
+Hints:
+ - To open several files in one window put a '+' in between the files.
+ - '@bw' after a map file displays the dots in a white to black gradient.
+ - '@bg' after a map file displays the dots in a grey to black gradient.
+ - '@b' after a map file displays the dots in black.
+ - '@r' after a map file displays the dots in red.
+ - '@g' after a map file displays the dots in green.
+ - '@m' after a map file displays the dots in magenta.
+ - Example: 'TOPPView 1.mzML + 2.mzML @bw + 3.mzML @bg'
+```
diff --git a/docs/images/introduction/hplc-mass-spectrometry-setup.png b/docs/images/introduction/hplc-mass-spectrometry-setup.png
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..bbe83186
Binary files /dev/null and b/docs/images/introduction/hplc-mass-spectrometry-setup.png differ
diff --git a/docs/images/introduction/openms-architecture.png b/docs/images/introduction/openms-architecture.png
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2f4b925d
Binary files /dev/null and b/docs/images/introduction/openms-architecture.png differ
diff --git a/docs/images/topp/command-line-call.png b/docs/images/topp/command-line-call.png
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..cb9c6444
Binary files /dev/null and b/docs/images/topp/command-line-call.png differ
diff --git a/docs/images/tutorials/knime/add-node-to-workspace.gif b/docs/images/tutorials/knime/add-node-to-workspace.gif
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7e638668
Binary files /dev/null and b/docs/images/tutorials/knime/add-node-to-workspace.gif differ
diff --git a/docs/images/tutorials/knime/connected-nodes-configured.png b/docs/images/tutorials/knime/connected-nodes-configured.png
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..dcff5c52
Binary files /dev/null and b/docs/images/tutorials/knime/connected-nodes-configured.png differ
diff --git a/docs/images/tutorials/knime/connected-nodes-not-configured.png b/docs/images/tutorials/knime/connected-nodes-not-configured.png
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9d9fc27c
Binary files /dev/null and b/docs/images/tutorials/knime/connected-nodes-not-configured.png differ
diff --git a/docs/images/tutorials/knime/output-file.png b/docs/images/tutorials/knime/output-file.png
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2e53e9f8
Binary files /dev/null and b/docs/images/tutorials/knime/output-file.png differ
diff --git a/docs/images/tutorials/knime/play-button.png b/docs/images/tutorials/knime/play-button.png
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..959d0d9b
Binary files /dev/null and b/docs/images/tutorials/knime/play-button.png differ
diff --git a/docs/images/tutorials/toppview/apply-topp-tool-to-layer.png b/docs/images/tutorials/toppview/apply-topp-tool-to-layer.png
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0824362e
Binary files /dev/null and b/docs/images/tutorials/toppview/apply-topp-tool-to-layer.png differ
diff --git a/docs/index.rst b/docs/index.rst
index 89f95730..ffca28fe 100644
--- a/docs/index.rst
+++ b/docs/index.rst
@@ -27,7 +27,6 @@ a unified parameter handling via a 'common tool description' (CTD) scheme.
data analysis framework that supports the generation of workflows for data analysis. Using a Common Tool Description
(CTD) file which is writeable by every TOPP tool and a node generator program (`Generic KNIME Nodes `_), all :term:`TOPP tools` can be made available to run in KNIME.
-
With :term:`pyOpenMS`, OpenMS offers Python bindings to a large part of the :term:`OpenMS API`
to enable rapid algorithm development. OpenMS supports the Proteomics Standard
Initiative (PSI) formats for MS data. The main contributors of OpenMS are
@@ -42,71 +41,63 @@ Contents
:caption: Introduction
:titlesonly:
- introduction
+ introduction/about-open-ms.md
+ introduction/background.md
+ introduction/how-openms-works.md
.. toctree::
:maxdepth: 2
- :caption: Getting Started
- :titlesonly:
+ :caption: Installation Guides
- installations/installation-on-gnu-linux
- installations/installation-on-windows
- installations/installation-on-macos
- installations/build-openms-from-source
+ installations/installation-on-gnu-linux.md
+ installations/installation-on-macos.md
+ installations/installation-on-windows.md
.. toctree::
:maxdepth: 2
- :caption: Quick Start Guides
- :titlesonly:
+ :caption: OpenMS Applications and Tools
- guides/user-guides/user-quickstart-guide
- guides/contributors-quickstart-guide.md
+ openms-applications-and-tools/openms-applications.md
+ openms-applications-and-tools/topp-tools.md
+ openms-applications-and-tools/utils-tools.md
+ openms-applications-and-tools/command-line-interface.md
+ openms-applications-and-tools/visualize-with-openms.md
.. toctree::
:maxdepth: 2
- :caption: Tutorials
- :titlesonly:
-
- tutorials/TOPP/TOPP-tutorial
- tutorials/TOPPAS/TOPPAS-tutorial
- tutorials/KNIME/KNIME-tutorial
-
-.. toctree::
- :maxdepth: 2
- :caption: OpenMS TOPP Tools
- :titlesonly:
+ :caption: Run Workflows with OpenMS Tools
- topp-and-utils/topp-and-utils.md
- topp-and-utils/adding-new-tool-to-topp.md
+ run-workflows-with-openms-tools/openms-in-knime.md
+ run-workflows-with-openms-tools/openms-in-nextflow.md
+ run-workflows-with-openms-tools/openms-on-galaxy.md
.. toctree::
:maxdepth: 2
- :caption: Developer Resources
- :titlesonly:
+ :caption: Tutorials and Quick Start Guides
- additional-resources/developer-guidelines-for-addding-new-dependent-libraries.md
- additional-resources/external-code-using-openms.md
- advanced-resources/custom-compilation.md
- advanced-resources/build-custom-openms-knime-package.md
+ tutorials-and-quickstart-guides/tutorials.md
+ tutorials-and-quickstart-guides/quickstart-guides.md
.. toctree::
:maxdepth: 2
- :caption: OpenMS GitHub Workflow
- :titlesonly:
+ :caption: Develop with OpenMS
- additional-resources/openms-git-workflow.md
- additional-resources/reporting-bugs-and-issues.md
- additional-resources/write-and-label-github-issues.md
- additional-resources/pull-request-checklist.md
+ develop-with-openms/openms-core-library.md
+ develop-with-openms/pyopenms.md
+ develop-with-openms/build-openms-from-source.md
+ develop-with-openms/link-external-code-to-openms.md
+ develop-with-openms/developer-tutorial.md
+ develop-with-openms/api-reference.md
.. toctree::
:maxdepth: 2
- :caption: Frequently Asked Questions
- :titlesonly:
-
- faqs/developer-faq.md
- faqs/contributor-faq.md
+ :caption: Contribute to OpenMS
+ contribute-to-openms/openms-git-workflow.md
+ contribute-to-openms/write-and-label-github-issues.md
+ contribute-to-openms/adding-new-tool-to-topp.md
+ contribute-to-openms/pull-request-checklist.md
+ contribute-to-openms/advanced.md
.. toctree::
:maxdepth: 2
@@ -116,16 +107,12 @@ Contents
.. toctree::
:maxdepth: 2
- :caption: Glossary
-
- glossary.md
-
-.. toctree::
- :maxdepth: 2
- :caption: Contact Us
-
- contact-us
+ :caption: Quick Reference
+ quick-reference/contributor-faq.md
+ quick-reference/developer-faq.md
+ quick-reference/contact-us.md
+ quick-reference/glossary.md
Indices and tables
==================
diff --git a/docs/installations/installation-on-gnu-linux.md b/docs/installations/installation-on-gnu-linux.md
index a8d7c3ed..cc76cabe 100644
--- a/docs/installations/installation-on-gnu-linux.md
+++ b/docs/installations/installation-on-gnu-linux.md
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-Installation on GNU/Linux
+GNU/Linux
=========================
## Install via Conda
diff --git a/docs/installations/installation-on-macos.md b/docs/installations/installation-on-macos.md
index 4e1769c3..8abfd65e 100644
--- a/docs/installations/installation-on-macos.md
+++ b/docs/installations/installation-on-macos.md
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-Installation on macOS
+macOS
====================
## Install via macOS installer
@@ -39,7 +39,7 @@ Make sure `` points to the folder where OpenMS is installed locally
## Install via Conda or Bioconda
-Follow [these](installation-on-gnu-linux.md#install-via-conda) instructions.
+Follow the [instructions](installation-on-gnu-linux.md#install-via-conda) .
## Build OpenMS from source
diff --git a/docs/installations/installation-on-windows.md b/docs/installations/installation-on-windows.md
index 9ba0b18a..5a5b41d5 100644
--- a/docs/installations/installation-on-windows.md
+++ b/docs/installations/installation-on-windows.md
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-Installation on Windows
+Windows
=======================
## Install via Windows installer
diff --git a/docs/introduction.md b/docs/introduction.md
deleted file mode 100644
index c8d6ef45..00000000
--- a/docs/introduction.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,119 +0,0 @@
-Introduction
-============
-
-[OpenMS](http://www.openms.org/)
-is an open-source software C++ library for {term}`LC-MS` data management and
-analyses. It offers an infrastructure for rapid development of mass
-spectrometry related software. OpenMS is free software available under the
-three clause BSD license and runs under Windows, macOS, and Linux.
-
-```{note}
-This introduction is aimed at users new to the field of LC-MS data analysis and will introduce some basics terms
-and concepts. How to handle the data analysis, available data structures, algorithms and more are covered in the various
-subsections of this documentation.
-```
-
-# Background
-
-Proteomics and metabolomics are interdisciplinary research fields that study structure, function, and interaction of
-proteins and metabolites. They employ large-scale experimental techniques that allow acquiring data at the level of
-cellular systems to whole organisms. Mass spectrometry combined with chromatographic separation is commonly used to
-identify, characterize or quantify the amount of proteins and metabolites.
-
-In mass spectrometry-based proteomics and metabolomics, biological samples are extracted, prepared, and separated to
-reduce sample complexity. The separated analytes are ionized and measured in the mass spectrometer. Mass and abundance
-of ions are stored in mass spectra and used to identify and quantify the analytes in the sample using computational
-methods. The quantity and identity of analytes can then be used, for instance, in biomarker discovery, medical diagnostics,
-or basic research.
-
-## Liquid Chromatography(LC)
-
-LC aims to reduce the complexity of the measured sample by separating analytes based on their physicochemical properties.
-Separating analytes in time ensures that a manageable amount of analytes elute at the same time. In mass
-spectrometry-based proteomics, (high-pressure) liquid chromatographic separation techniques (HPLC) are methods of choice
-to achieve a high degree of separation. In HPLC, {term}`peptides` are separated on a column. Solved in a pressurized liquid
-(mobile phase) they are pumped through a solid adsorbent material (stationary phase) packet into a capillary column.
-Physicochemical properties of each peptide determine how strongly it interacts with the stationary phase. The most
-common HPLC technique in proteomics and metabolomics uses reversed-phase chromatography (RPC) columns. RPC employs a
-hydrophobic stationary phase like {term}`octadecyl (C18)`, a nonpolar carbon chain bonded to a silica base, and a polar mobile
-phase. Polar molecules interact weakly with the stationary phase and elute earlier, while non-polar molecules are retained.
-Interaction can be further modulated by changing the gradient of solvent concentration in the mobile phase over time.
-Elution times in LC are inherently prone to variation, for example, due to fluctuations in the flow rate of the mobile
-phase or change of column. Retention time shifts between runs may be compensated using computational chromatographic
-retention time alignment methods. In the {term}`LC-MS` setup, the column is directly coupled to the ion source of the mass
-spectrometer.
-
-
-
-## Mass Spectrometry
-
-MS is an analytical technique used to determine the {term}`mass` of molecules. In order to achieve highly accurate and sensitive
-mass measurements at the atomic scale, mass spectrometers manipulate charged particles using magnetic and electrostatic
-fields.
-
-
-
-In a typical mass spectrometer, three principal components can be identified:
-
-- **Ion Source**: A mass spectrometer only handles {term}`ions`. Thus, charge needs first be transferred to uncharged
- particles. The component responsible for the ionization is the ion source. Different types of ion sources and ionization
- techniques exist with {term}`electrospray ionization (ESI)` being currently the most widely used ionization technique
- for mass spectrometry-based proteomics.
-
-- **Mass Analyzer**: Most commonly used mass analyzer in proteomics are {term}`time-of-flight (TOF)` mass analyzers,
- {term}`quadrupole mass filters`, and {term}`orbitrap analyzers`. In TOF mass analyzers, the ions are accelerated in an electric field.
- The flight time of an ion allows calculating the velocity which in turn is used to calculate the mass-to-charge ratio
- (m/z). Varying the electric field allows filtering certain mass-to-charge ratios before they enter the detector. In
- quadrupole mass filters, ions pass through an oscillating electric field created by four parallel rods. For a
- particular voltage, only ions in a certain mass-to-charge range will reach the detector. The orbitrap is an ion trap
- mass analyzer (and detector) that traps ions in orbital motion between a barrel-like outer electrode and a spindle-like
- central electrode allowing for prolonged mass measurement. As a result of the prolonged mass measurements, a high mass
- resolution can be achieved.
-
-- **Detector**: The last component of the mass spectrometer is the detector. It determines the abundance of ions that
- passed through the mass analyzer. Ion intensities (a value that relates to its abundance) and the mass-to-charge ratio
- are recorded in a mass spectrum.
-
-A sample is measured over the retention time of the chromatography typically resulting in tens of thousands of spectra.
-The measurement of one sample is called an MS run and the set of spectra called an {term}`MS(1)` map or peak map.
-
-
-
-The left image displays spectrum with peaks (m/z and intensity values) and the right image shows spectra stacked in
-retention time yielding a peak map.
-
-In proteomics and metabolomics, the {term}`MS(1)` intensity is often used for the quantification of an analyte. Identification
-based on the {term}`MS(1)` mass-to-charge and the isotope pattern is highly ambiguous. To improve identification, tandem mass
-spectrometry {term}`(MS/MS)` can be applied to assess the analyte substructure. To this end, the precursor ion is isolated and
-kinetically fragmented using an inert gas (e.g., Argon). Fragments produced by {term}`collision-induced dissociation (CID)`
-are stored in an {term}`MS^2` (or {term}`MS/MS`) spectrum and provide information that helps to resolve the ambiguities in identification.
-Alternatively, {term}`MS/MS` spectra can be used for quantification.
-
-Get started with installing OpenMS using the installers available for different operating systems!
-
-## Installation on different platforms
-
-```{tab} GNU/Linux
-
-```bash
-wget https://abibuilder.informatik.uni-tuebingen.de/archive/openms/OpenMSInstaller/release/latest/OpenMS-2.8.0-Debian-Linux-x86_64.deb
-
-```
-
-```
-
-```{tab} Windows
-
-```bash
-wget https://abibuilder.informatik.uni-tuebingen.de/archive/openms/OpenMSInstaller/release/latest/OpenMS-2.8.0-Win64.exe
-```
-
-```
-
-```{tab} macOS
-
-```bash
-wget https://abibuilder.informatik.uni-tuebingen.de/archive/openms/OpenMSInstaller/release/latest/OpenMS-2.8.0-macOS.dmg
-```
-
-```
diff --git a/docs/introduction/about-open-ms.md b/docs/introduction/about-open-ms.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..abbff286
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/introduction/about-open-ms.md
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
+What is OpenMS?
+===============
+
+OpenMS is an open-source software platform designed for the analysis and visualization of high-throughput mass spectrometry data. OpenMS has been designed to operate on all platforms, and provides a flexible framework for users to access a wide range of built-in tools or build their own tools using the existing functionality. These tools can be applied separately to data or be applied in sequence (as a workflow or pipeline) to mass spectrometry data. OpenMS is well established and has been used widely in [literature](https://openms.github.io/publications/), particularly in the life sciences.
+
+Fields such as proteomics and metabolomics require the rapid, large-scale identification, quantification and characterization of biomolecules which traditional analytical techniques struggle to offer. OpenMS has been created by a team of biologists and computer scientists to create a completely open-source solution that offers customisable tools for high-throughput processing of mass spectrometry data.
+
+OpenMS provides a number of tools built from a C++ core library. These tools are collectively referred to as “The OpenMS PiPeline (TOPP) (formerly known as The OpenMS Proteomic Pipeline) tools. TOPP tools can be chained in a sequence to form workflows and can be applied to mass spectrometry data.
+Note: TOPP’s capabilities have been expanded to apply to a wide range of areas in the life sciences.
diff --git a/docs/introduction/background.md b/docs/introduction/background.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..bfd913f7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/introduction/background.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+Background
+==========
+
+OpenMS was primarily designed to process, analyze and visualize liquid chromatography - mass spectrometry (LC-MS) data.
+
+```{note}
+OpenMS in recent times has been expanded to include other mass spectrometry methods. To design your experimental analysis solution, [contact the OpenMS team](../quick-reference/contact-us.md) today.
+```
+
+To understand how to use OpenMS, one must have a basic understanding of an LC-MS setup.
+
+
+## Liquid Chromatography (LC)
+
+Liquid chromatography is an analytical technique used to separate analytes according to their physicochemical properties. A sample is transported via a liquid (known as the mobile phase) through a stationary phase which is packed into a capillary column. The time it takes for a separated analyte to move through the stationary phase (or how long it takes to elute) is known as its {term}`retention time`. Each analyte will have a different retention time, depending on how strongly the analyte interacts with the stationary phase. The total amount of analyte eluting from the column at every (retention) time point can be plotted as a {term}`chromatogram`. In LC-MS, the measured ion intensities are used as a proxy for the total amount.
+
+
+
+## Mass Spectrometry
+
+Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique used to determine the abundance of molecules in a sample. There are three major components in a mass spectrometer:
+- An **ion source**, which generates ions from the incoming sample.
+- A **mass analyzer**, which separates the ions according to their mass-to-charge ratio. There are several types of mass analyzers. Depending on the mass analyzer used in the experiment, OpenMS offers calibration tools, so that highly accurate results can be achieved.
+- A **detector**, which records the mass-to-charge ratio of each ion against their relative abundance in a plot known as a {term}`mass spectrum`.
+
+
+
+## Liquid Chromatography - Mass Spectrometry
+Liquid chromatography is often coupled with mass spectrometry in order to reduce complexity in the mass spectra. The separated analytes from the liquid chromatography setup are directly injected into the ion source from the mass spectrometry setup. Multiple analytes that elute at the same time are separated by mass using the mass spectrometer.
+
+
diff --git a/docs/introduction/how-openms-works.md b/docs/introduction/how-openms-works.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0fc18ea2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/introduction/how-openms-works.md
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+How OpenMS Works
+================
+
+OpenMS has been structured so that users from a wide range of fields can access what they need to solve their particular problem, depending on their skillset.
+
+The following entry points for OpenMS and its TOPP tools are available for users:
+- **Download the OpenMS C++ core library**
+
+ As shown in the image below, TOPP tools have been created using the OpenMS core library and some external libraries, which are written in C++. Using the OpenMS core library directly provides faster access to tools and shorter run-times. Additional TOPP tools can also be developed, customized or extended based on the user’s needs. View the instructions to download the OpenMS core library here.
+- **Install the pyOpenMs python library**
+
+ Classes and methods originally written in C++ have been exposed to a Python interface (pyOpenMS) using python bindings. pyOpenMS was created for users with Python knowledge who want to quickly prototype new methods. View the instructions to install pyOpenMS here.
+
+- **Use command-line tools**
+
+ All TOPP tools can be executed from a Command Line Interface (CLI) directly or using a shell script. By using a CLI, users can easily automate tasks and create workflows that can be saved, stored and used on multiple datasets. Command line interfaces include, but are not limited to PowerShell in Windows or Terminal in Linux or macOS. View the command-line usage quick start guide here.
+
+- **Use OpenMS graphical applications**
+
+ When OpenMS is installed, a number of graphical user interfaces are available. Life science experts that want to quickly process their mass spectrometry data with the TOPP tools available can use this option. View the instructions to install OpenMS here.
+
+- **Use a supported workflow editor**
+
+ Suppose you want to run the same sequence of TOPP tools on a number of data sets. You can use applications such as KNIME and Galaxy (where TOPP tools are available as a plugin), to apply predefined workflows or custom workflows you have designed on your data. KNIME and Galaxy are recommended over TOPPAS, which can also be used to create workflows however is no longer supported.
diff --git a/docs/openms-applications-and-tools/command-line-interface.md b/docs/openms-applications-and-tools/command-line-interface.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2969b3f5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/openms-applications-and-tools/command-line-interface.md
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+Command Line Interface
+======================
+
+TOPP tools are designed to be called from the command line. OpenMS provides a Command Line Interface (CLI) called TOPP shell to easily execute TOPP tools on mass spectrometry data. However, you can configure the CLI of your choice to run TOPP tools.
+
+Command line calls will depend on the TOPP tools used, as each TOPP tool has its own set of parameters. However, the following arguments are typically used:
+
+- `-in`
+
+ Specify an input file in the command line using the `-in` argument. The input file should have an mzML format. If not, use the file converter to convert the file to one using an mzML format. For more information, view the file handling documentation.
+- `-out`
+
+ Specify an output file in the command line using the `-out` argument. The output file should have an mzML format, the same format as the input file.
+- `-ini`
+
+ Specify an INI file in the command line using the `-ini` argument. TOPP uses INI files to set parameters specific to the command line tool being called.
+- `-write_ini`
+
+ Create an INI file using the `-write_ini` file argument.
+ Create an INI file with this call:
+ ` -write_ini `
+ If you want a visual tool to assist setting parameters, use [INIFileEditor](graphical-topp-tools/ini-file-editor.md), an application provided when you download OpenMS. Otherwise, you can set the parameters from the command line.
+- `-help`
+
+ Get information about basic options related to the tool using the -help parameter. For more advanced options (algorithmic parameters), use `--help`.
+- `--help`
+
+ Get detailed information about algorithmic parameters using the `--help` parameter.
+
+Many (but not all) command line calls will have the following structure:
+
+```bash
+ -in -out -ini
+```
+
+The following command line call uses the FileFilter tool to extract data from an mzML file. Note, that this call directly specifies the tool-specific parameters and doesn’t rely on an INI file:
+
+
diff --git a/docs/openms-applications-and-tools/openms-applications.md b/docs/openms-applications-and-tools/openms-applications.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..448a6733
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/openms-applications-and-tools/openms-applications.md
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
+OpenMS Applications
+===================
+
+OpenMS provides a suite of applications, designed for users who want easy access to TOPP tools. These applications include:
+- **INIFileEditor**
+
+ A GUI application used to edit INI files. INI files are files with the extension .ini and are common configuration files for all TOPP tools.
+
+- **TOPP shell**
+
+ A Command Line Interface (CLI) that provides easy access to tools. Users don’t need to use TOPP shell; instead, they can configure their own CLI to directly use TOPP tools.
+- **TOPPView**
+
+ A GUI application used to inspect, visualize and compare mass spectrometry data. Read more in-depth documentation about TOPPView.
+
+- **TOPPAS (deprecated)**
+
+ A GUI application used to apply multiple tools sequentially on mass spectrometry data. Applying multiple tools in a sequence is referred to as a workflow or a pipeline. OpenMS no longer supports TOPPAS and instead recommends the use of [KNIME](https://www.knime.com/), for which we provide a community plugin.
+
+- **SwathWizard**
+An application for SWATH analysis. SwathWizard is used to analyze DIA swath data.
diff --git a/docs/openms-applications-and-tools/topp-tools.md b/docs/openms-applications-and-tools/topp-tools.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..49596b8d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/openms-applications-and-tools/topp-tools.md
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
+TOPP Tools
+==========
+
+The following sections introduce TOPP, some general concepts and more specific information regarding each tool.
+
+```{toctree}
+:maxdepth: 1
+
+topp-tools/introduction-to-topp.md
+topp-tools/key-concepts.md
+topp-tools/types-of-topp-tools.md
+
+```
diff --git a/docs/openms-applications-and-tools/topp-tools/introduction-to-topp.md b/docs/openms-applications-and-tools/topp-tools/introduction-to-topp.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c4217c7b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/openms-applications-and-tools/topp-tools/introduction-to-topp.md
@@ -0,0 +1,6 @@
+Introduction to TOPP
+====================
+
+OpenMS provides a vast array of tools called TOPP tools that automate typical mass processing tasks. They can be either:
+- Executed from the command line or,
+- Applied using graphical applications.
diff --git a/docs/openms-applications-and-tools/topp-tools/key-concepts.md b/docs/openms-applications-and-tools/topp-tools/key-concepts.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..24a7e0f4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/openms-applications-and-tools/topp-tools/key-concepts.md
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
+Key Concepts
+============
+
+Before using TOPP tools, there are a number of concepts to understand. These include:
+- **TOPP INI files**
+
+ TOPP INI files are XML-based files with an `.ini extension`. OpenMS uses TOPP INI files to set parameters for one or more TOPP tools. Alternatively, the command line can be used to set TOPP tool parameters.
+ Here is an example of a TOPP INI file:
+
+ ```xml
+
+
+
+
+
+ - Go to File > Install KNIME Extensions.
+ - Search for OpenMS.
+ - Select the checkbox next to OpenMS and click Next.
+ - Click Next.
+ - Accept the terms of conditions.
+ - Restart KNIME
+
+
+**2. Open a new file** by going to **File** > **New file**.
+
+**3. Construct workflow by adding nodes.**
+
+ - Go to the Node repository
+ - In the search field, type Input File. You should see an Input File node in the filtered list.
+ - Drag and drop the Input File node from the Node repository into the workspace.
+ 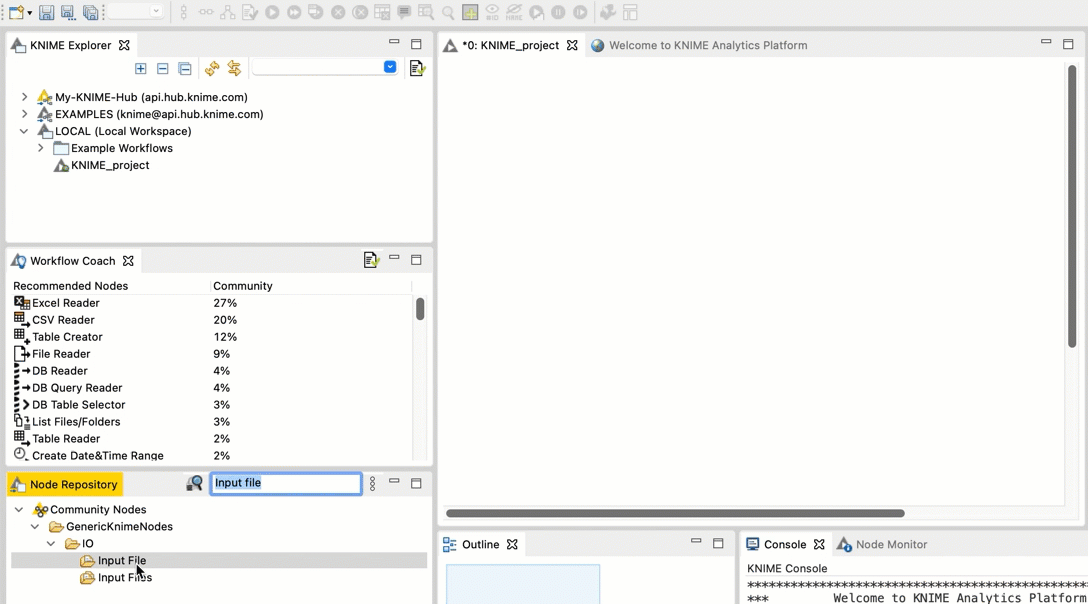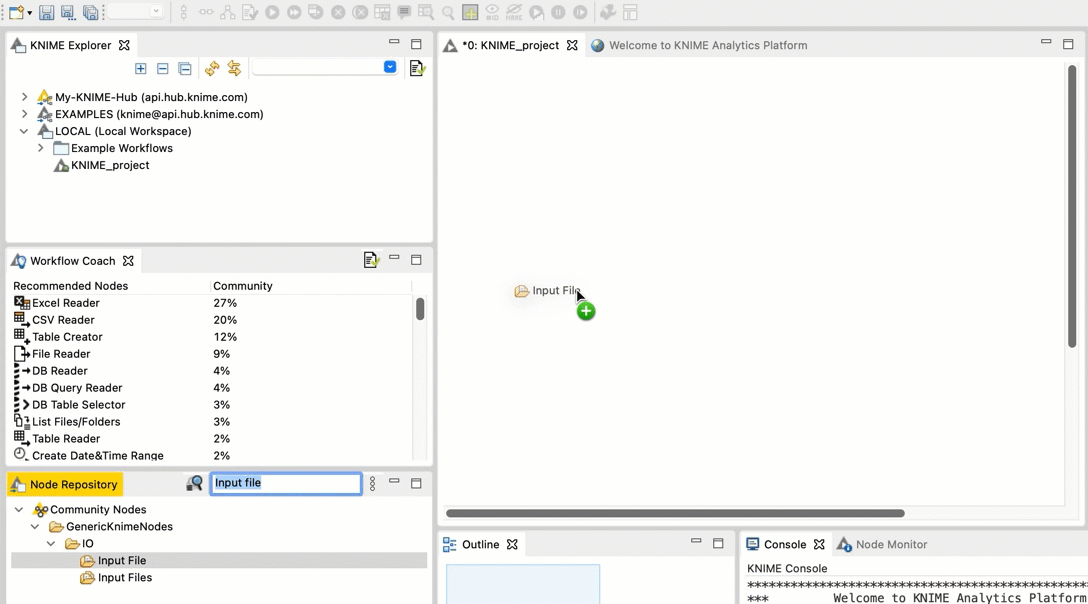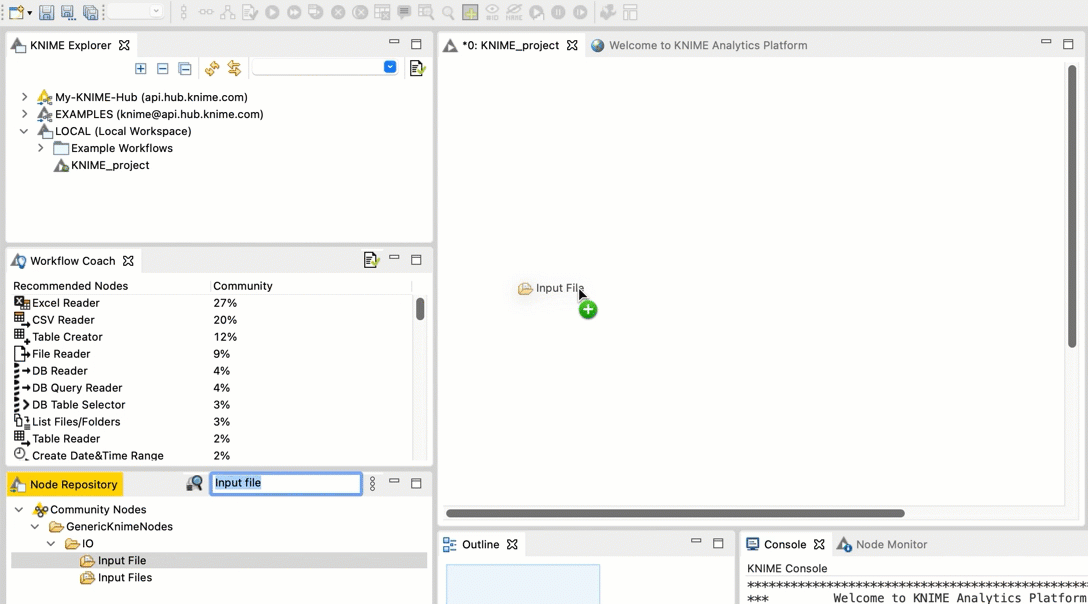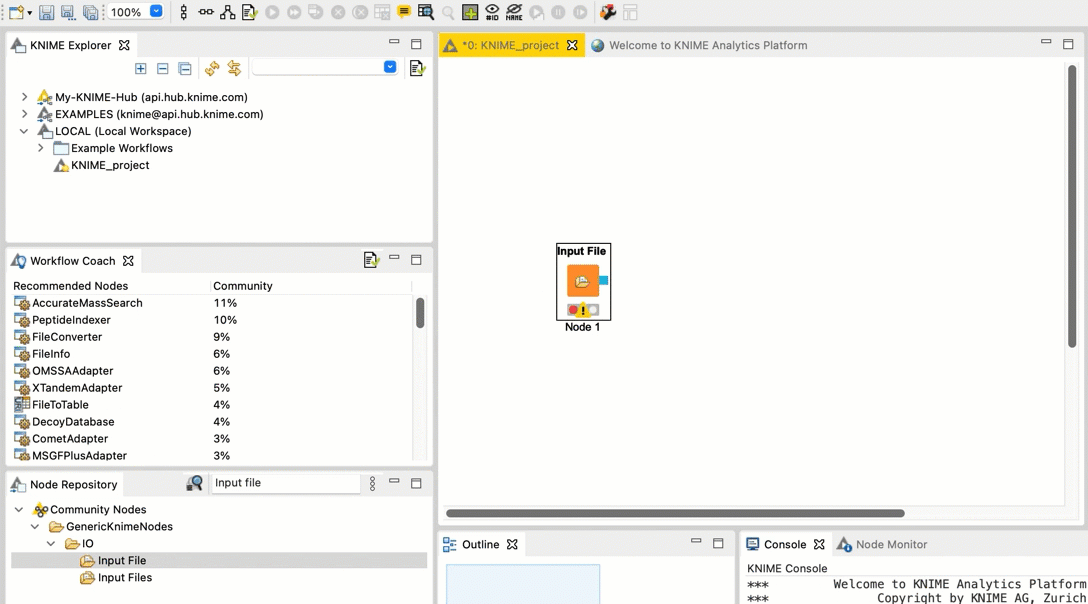 +
+ - Repeat steps b and c for the FileInfo node and the Output File node.
+ - Connect the Input File node to the FileInfo node. Connect the FileInfo node to the Output File node. Your workflow should look like this:
+ 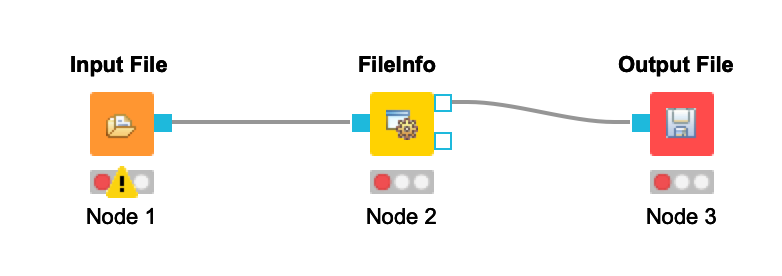 + Once you configure your nodes in the next step, the warnings should disappear.
+
+ Once you configure your nodes in the next step, the warnings should disappear.
+
+
+**4. Configure the nodes in workflow.**
+
+ - Right-click the Input File node and select Configure.
+ - Click Browse and choose the appropriate file from the file importer.
+ - Click OK.
+ - Right-click the Output File node and select Configure.
+ - Either choose an existing file or enter the file name of the new file. If you choose an existing file, select the Overwrite file(s) if it/they exist checkbox.
+ - Click OK.
+ - Your workflow should be cleared of warnings and look like this:
+ 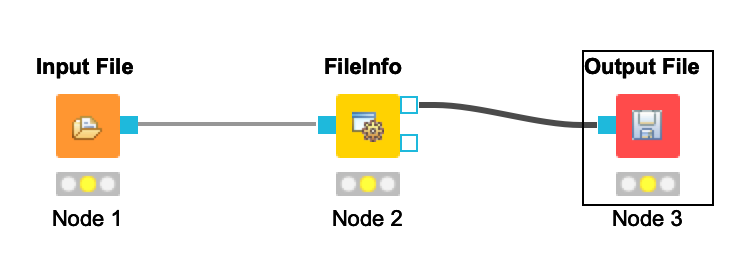 +
+
+
+**5. Play the workflow.**
+
+ - Click the Execute all executable nodes
 button in the toolbar at the top of the screen.
button in the toolbar at the top of the screen.
+ - You should produce an output file at the specified location. Here is an example of what can be produced:
+ 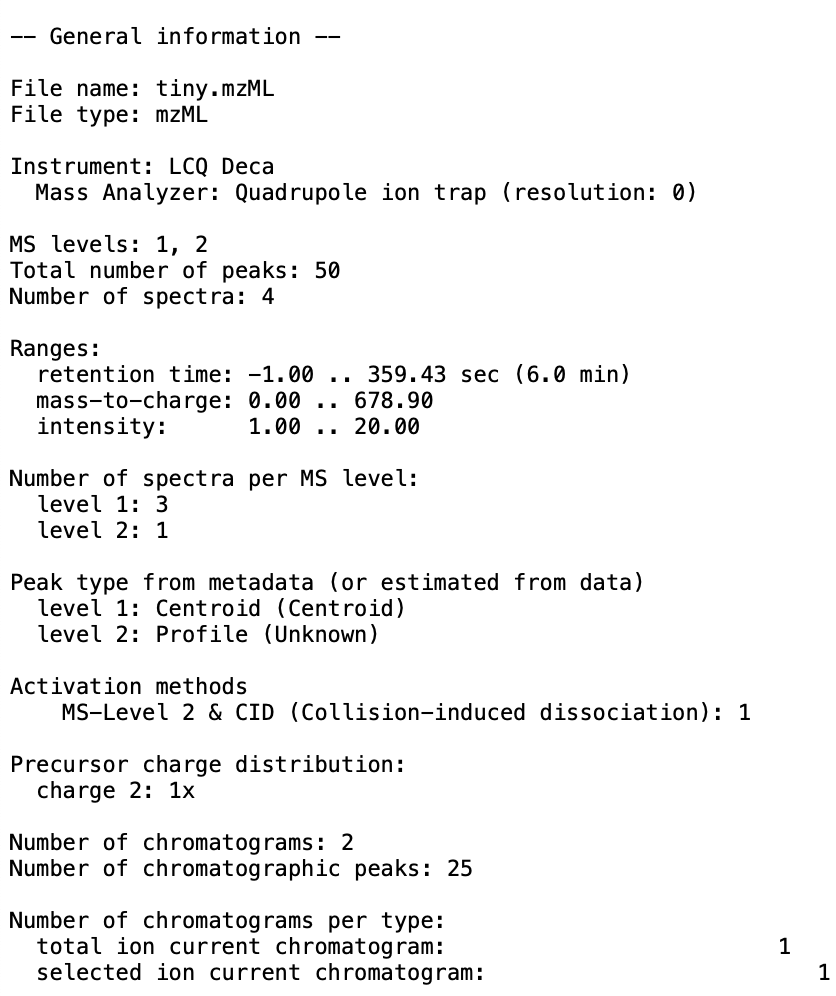 +
+
 +
+  + Once you configure your nodes in the next step, the warnings should disappear.
+
+ Once you configure your nodes in the next step, the warnings should disappear.
+  +
+  button in the toolbar at the top of the screen.
+
button in the toolbar at the top of the screen.
+  +
+