Website • Docs • Installation • Daft Quickstart • Community and Support
Daft is a high-performance data engine for AI and multimodal workloads. Process images, audio, video, and structured data at any scale.
- Native multimodal processing: Process images, audio, video, and embeddings alongside structured data in a single framework
- Built-in AI operations: Run LLM prompts, generate embeddings, and classify data at scale using OpenAI, Transformers, or custom models
- Python-native, Rust-powered: Skip the JVM complexity with Python at its core and Rust under the hood for blazing performance
- Seamless scaling: Start local, scale to distributed clusters on Ray, Kubernetes, or Daft Cloud
- Universal connectivity: Access data anywhere (S3, GCS, Iceberg, Delta Lake, Hugging Face, Unity Catalog)
- Out-of-box reliability: Intelligent memory management and sensible defaults eliminate configuration headaches
Install Daft with pip install daft. Requires Python 3.10 or higher.
For more advanced installations (e.g. installing from source or with extra dependencies such as Ray and AWS utilities), please see our Installation Guide
Get started in minutes with our Quickstart - load a real-world e-commerce dataset, process product images, and run AI inference at scale.
- Examples - see Daft in action with use cases across text, images, audio, and more
- User Guide - take a deep-dive into each topic within Daft
- API Reference - API reference for public classes/functions of Daft
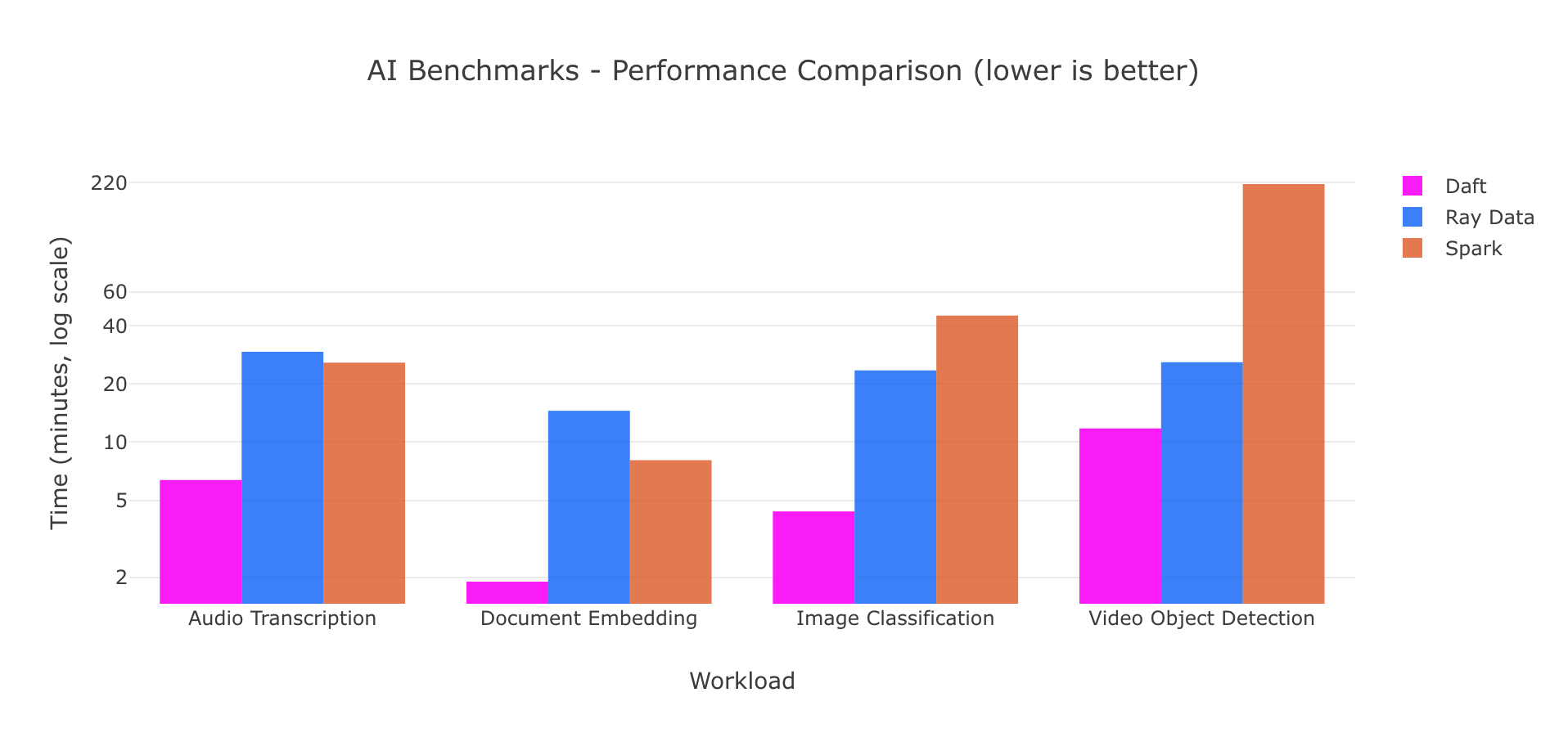
To see the full benchmarks, detailed setup, and logs, check out our benchmarking page.
We <3 developers! To start contributing to Daft, please read CONTRIBUTING.md. This document describes the development lifecycle and toolchain for working on Daft. It also details how to add new functionality to the core engine and expose it through a Python API.
Here's a list of good first issues to get yourself warmed up with Daft. Comment in the issue to pick it up, and feel free to ask any questions!
To help improve Daft, we collect non-identifiable data via Scarf (https://scarf.sh).
To disable this behavior, set the environment variable DO_NOT_TRACK=true.
The data that we collect is:
- Non-identifiable: Events are keyed by a session ID which is generated on import of Daft
- Metadata-only: We do not collect any of our users’ proprietary code or data
- For development only: We do not buy or sell any user data
Please see our documentation for more details.
| Engine | Query Optimizer | Multimodal | Distributed | Arrow Backed | Vectorized Execution Engine | Out-of-core |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daft | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Pandas | No | Python object | No | optional >= 2.0 | Some(Numpy) | No |
| Polars | Yes | Python object | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Modin | Yes | Python object | Yes | No | Some(Pandas) | Yes |
| Ray Data | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Some(PyArrow) | Yes |
| PySpark | Yes | No | Yes | Pandas UDF/IO | Pandas UDF | Yes |
| Dask DF | No | Python object | Yes | No | Some(Pandas) | Yes |
Daft has an Apache 2.0 license - please see the LICENSE file.