-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 3.8k
Split node min range is not stringent. #4885
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
Closed
Closed
Changes from all commits
Commits
Show all changes
5 commits
Select commit
Hold shift + click to select a range
5cb0451
Set split node's range to minimum of ext and split factor.
yongfeng-nv df93c30
Add a test function to ensure that stringent (8 instead of 32) range …
yongfeng-nv d1e101e
Update an existing test. Otherwise, it fails with the split node min…
yongfeng-nv cdd6fd1
Update a helper function name.
yongfeng-nv 8ff3b4f
Apply the same change to set split node's range for nparts.
yongfeng-nv File filter
Filter by extension
Conversations
Failed to load comments.
Loading
Jump to
Jump to file
Failed to load files.
Loading
Diff view
Diff view
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
Add this suggestion to a batch that can be applied as a single commit.
This suggestion is invalid because no changes were made to the code.
Suggestions cannot be applied while the pull request is closed.
Suggestions cannot be applied while viewing a subset of changes.
Only one suggestion per line can be applied in a batch.
Add this suggestion to a batch that can be applied as a single commit.
Applying suggestions on deleted lines is not supported.
You must change the existing code in this line in order to create a valid suggestion.
Outdated suggestions cannot be applied.
This suggestion has been applied or marked resolved.
Suggestions cannot be applied from pending reviews.
Suggestions cannot be applied on multi-line comments.
Suggestions cannot be applied while the pull request is queued to merge.
Suggestion cannot be applied right now. Please check back later.
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
Can you explain the reason for these changes?
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
Sure. Before the test change, thread_y are bound to stage Conv's 3rd IterVar, n.outer.inner ranging in [0, 0], and W.shared's 3rd, ax3.outer ranging in [0, 1], as shown blow. These two stages are in one kernel.
Without my change, although its parent's ext is only 1, n.outer.inner is set to [min=0, ext=2], because the split factor is 2. n.outer.inner and ax3.outer's are allowed to bind to the same thread, as their ranges match.
With my change, n.outer.inner's range is set to [min=0, ext=1]. Ranges are different and both IterVars can't bind to the same thread. I got this error:
Similar problems happen to other IterVars binding to threadIdx.y and threadIdx.z.
Stop binding Apad.shared and W.shared's IterVars to threadIdx.y and threadIdx.z avoids such problem. The generated code are different. I attach them at the end. Let me show some diff first. Old code is on the left, new on the right. Here are the first two sets of diff:
The fill fragment part benefits from this PR. However, since I removed thread binding for Apad.shared and W.shared, the second diff show some regression -- more memory copying.
These are the last sets of diff:
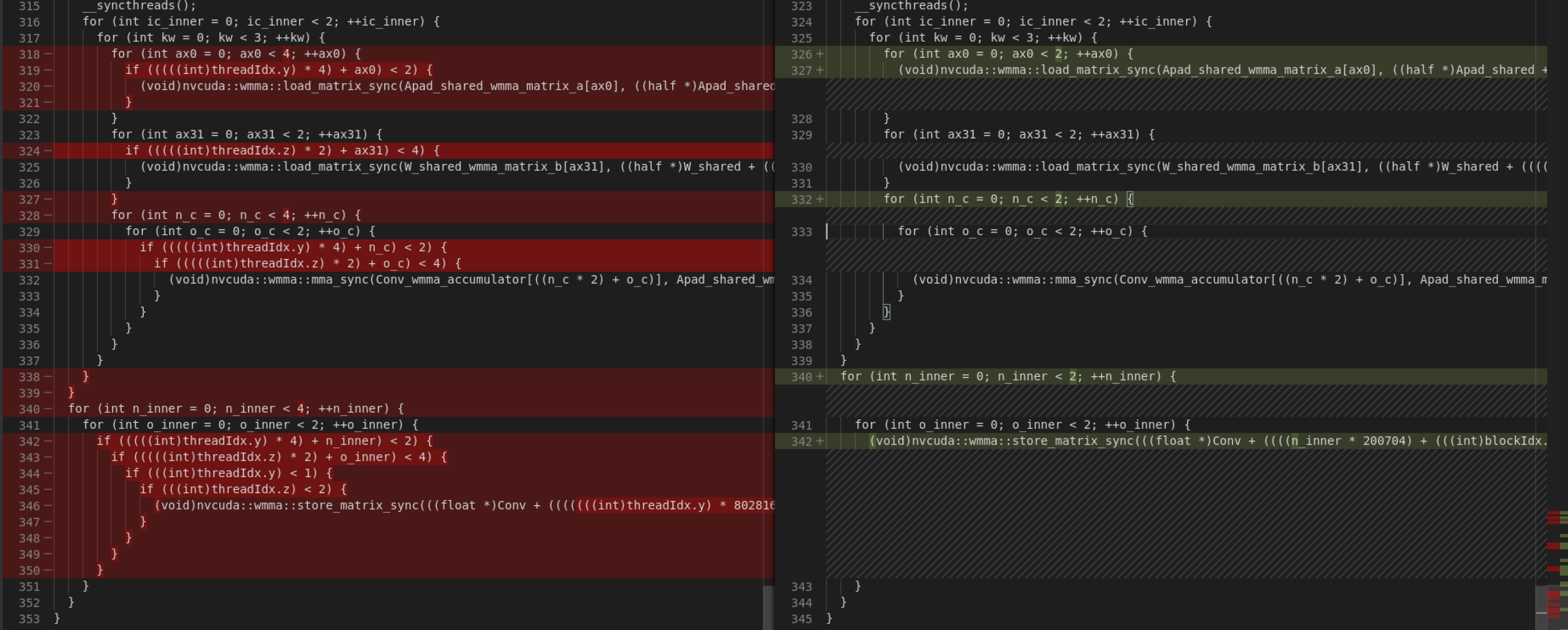
The new code look more concise than the old one in all these cases.
Overall, the test shows running time reduces from 0.060 ms to 0.035 ms. I haven't done other performance checking.
This PR makes auto bound inference more accurate/reasonable. However, this old test seems using split to force n.outer.inner's range to be larger than necessary. This PR changes this behavior of split, making it less expressive. Is this behavior a semantics by design?
A more general use case for threads binding: we would like to have a kernel with multiple stages to use same threads differently in each stage. For example, some stages need more threads than others. We don't mind allocating enough threads to satisfy the most demanding stage. But we also want to avoid unnecessary traversal (e.g. the likely statements) or memory allocation (e.g. Conv_wmma_accumulator shown above) due to the extra range. Is there a good way to achieve both?
Attach the entire generated CUDA code blow.
Before:
After:
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
I see. It is my fault to make such a "wrong" testcase. Thank you for finding and fixing it.
However, this "bug" shows two discuss points about this PR:
Possibility in thread binding
If we still want to bind the loops, which have different extents, to the same threadIdx. Can we make it after this PR?
Before
After
This case is really rare. So it will not block the PR merging but worths to think about it.
Schedule in AutoTVM
Today, we can make sure the schedule is correct (maybe slow but it can run) in different sizes.
In AutoTVM, We will search for many schedules and most of them will contain imperfect split. So, there will be more failure cases after this PR, although they are almost bad schedules. I'm not sure whether it will influence the cost model.
Generally, these two cases are not common in most uses. So I will approve this PR after CI's green. I just remind you of these and like to listen to your thought.
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
I have similar questions, especially echo on your first one. I didn't know how to schedule your example properly until I read your code. After my change, I don't know how to do that. That's why I wonder whether this behavior of split is by design or just a work around. How about bringing this discussion to the forum to get insight from @tqchen and more people.
My intuition to your second question is that my PR is neutral. While it disallows certain schedules, it also enables/improves others. When we think about auto scheduling, it may be more helpful. Fundamentally, we need to address the first question. AutoTVM will benefit from this PR, once we can express more requests about thread binding and infer bounds more accurately at the same time.
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
That‘s great. Can you create a discussion thread in https://discuss.tvm.ai?