Snapshot manager (snapm) manages named snapshot sets on Linux systems. Each snapshot set captures coordinated snapshots across multiple volumes, representing a consistent point-in-time system state that can be referenced and managed as a single unit.
- Coordinated snapshot sets: Create coordinated snapshots across multiple volumes
- Bootable snapshots: Generate boot entries for snapshot boot and failsafe revert
- Multiple backends: Support for LVM2 (Copy-on-Write and Thin) and Stratis
- Flexible scheduling: Integration with systemd timers for automated snapshot creation with retention policies
- Size policies: Flexible snapshot sizing with multiple strategies
- Difference engine: Compare snapshot sets to identify added, removed, moved, and modified files with multiple output formats
- Plugin architecture: Extensible design for additional storage backends
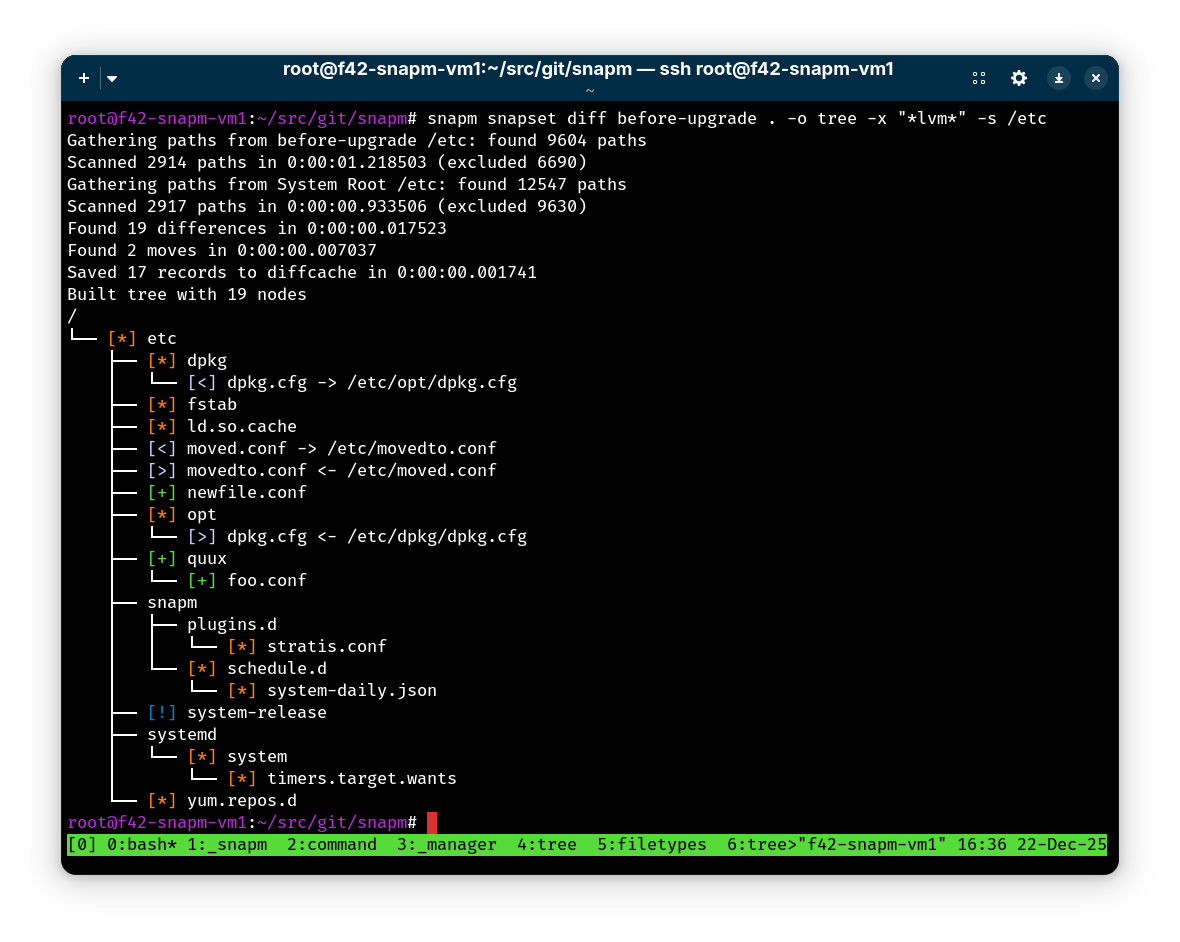
Compare a snapshot set to the running system with a hierarchical tree view:
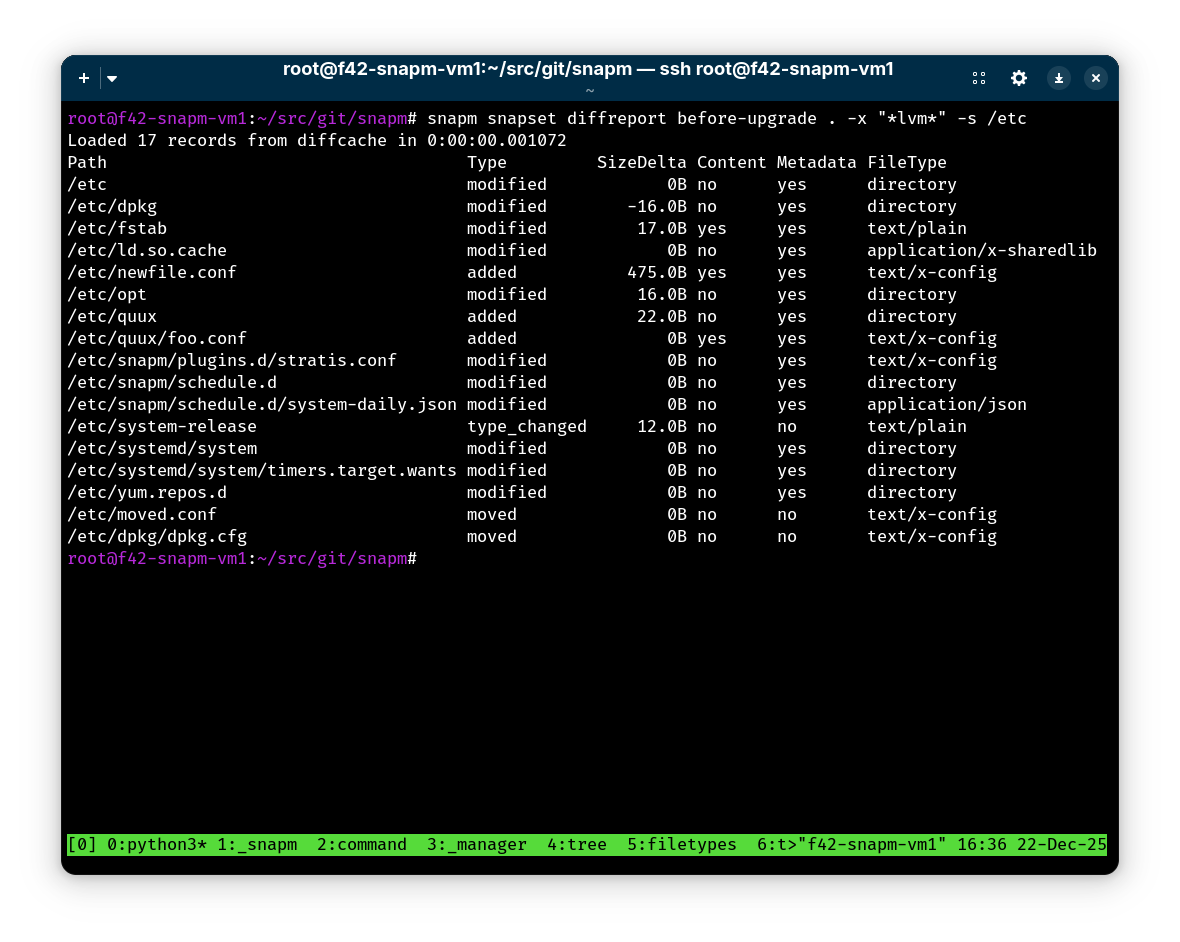
Generate tabular reports of changes between snapshot sets:
Install from distribution repositories (when available):
dnf install snapm boom-boot- Create and activate a virtual environment:
python3 -m venv --system-site-packages .venv && source .venv/bin/activate- If
boom-bootis not installed from your distribution's packages, clone and install it withpip:
git clone https://github.com/snapshotmanager/boom-boot.git
cd boom-boot
python3 -m pip install .- Repeat the process with the
snapmrepository:
git clone https://github.com/snapshotmanager/snapm.git
cd snapm
python3 -m pip install .Create a snapshot set named "before-upgrade" of root and home, with snapshot boot and revert boot entries:
snapm snapset create --bootable --revert before-upgrade / /homesnapm snapset listShow detailed information:
snapm snapset show before-upgrade- Reboot and select the snapshot boot entry from the GRUB menu
- Entry will be named: "Snapshot before-upgrade YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS (version)"
- Optionally run
grub2-reboot <title>to pre-select snapshot boot entry, e.g.:
grub2-reboot "Snapshot before-upgrade YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS (version)"- Use
grub-rebootinstead ofgrub2-rebooton Debian and Ubuntu systems.
snapm snapset revert before-upgradeThen reboot into the Revert boot entry.
Note: Reverting destroys the snapshot set (snapshots are merged back into the origin volumes).
Delete snapshot set when no longer needed:
snapm snapset delete before-upgradeBefore major system updates:
snapm snapset create --bootable --revert pre-update / /varIf update goes wrong, revert:
snapm snapset revert pre-updateWhen satisfied with update, clean up:
snapm snapset delete pre-updateQuick development checkpoint:
snapm snapset create dev-checkpoint /home /varContinue working...
If needed, revert specific volumes by splitting them into a dedicated snapshot set first:
snapm snapset split dev-checkpoint dev-checkpoint-home /homeExample output:
SnapsetName: dev-checkpoint-home
Sources: /home
NrSnapshots: 1
Time: 2025-08-30 12:44:00
UUID: ee82269f-8c78-5814-b47a-b9be31bcebb5
Status: Inactive
Autoactivate: no
Bootable: no
snapm snapset revert dev-checkpoint-homeAlternatively revert the entire snapshot set:
snapm snapset revert dev-checkpointCompare a snapshot set to the current system to see what changed:
snapm snapset diff pre-update .View changes as a hierarchical tree (default):
snapm snapset diff --output-format tree pre-update .Generate a unified diff of modified file contents:
snapm snapset diff --output-format diff pre-update .Get a summary of change counts:
snapm snapset diff --output-format summary pre-update .Export changed paths for use with other tools:
snapm snapset diff --output-format paths pre-update . | xargs tar cvf changes.tarGenerate a tabular report of differences:
snapm snapset diffreport -o path,type,size_delta pre-update .- User Guide - Comprehensive usage documentation
- API Documentation - Auto-generated API docs
- Manual Pages - System manual pages
- Linux system with LVM2 or Stratis volumes
- boom-boot
- Root privileges for performing storage operations
- Python 3.9+
| Backend | Type | Snapshots | Thin Provisioning | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LVM2 | Copy-on-Write | ✓ | ✗ | Stable |
| LVM2 Thin | Thin Pools | ✓ | ✓ | Stable |
| Stratis | Thin Pools | ✓ | ✓ | Stable |
We welcome contributions! Please see CONTRIBUTING.md for guidelines.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0. See LICENSE for details.
The Snapshot Manager logo incorporates an image of Tux, the Linux mascot originally conceived and designed by Larry Ewing.
- boom - Boot manager for Linux snapshot boot
- stratis-cli - Command-line tool for Stratis storage
- lvm2 - The LVM2 logical volume manager